At 3D Genetics we use an innovative and scientifically sound process to undertake our genetic selection and genetic improvement program. This process is composed of three main steps:
Collection of Phenotypes and Genotypes
Genetic Analysis
MateSel - Mate selection software
1. Phenotype and Genotype collection
50k SNP Chip
“A large, structured progeny test that now on an annual basis follows greater than 10,000 animals sired by 3D Genetics bulls progressively through their life collecting data of economic importance.”
The 3D Genetics phenotype collection process involves a large, structured progeny test program that now on an annual basis follows greater than 10,000 animals sired by 3D Genetics bulls progressively through their life collecting data on traits of economic importance.
Phenotype collection includes both measurements of the Live animal and Carcase respectively. All animals in the progeny test program have biological samples collected for subsequent DNA genotyping.
Live animal phenotypes.
Live animal phenotypes are collected from these animals that are run in large contemporary groups through their entire lives commencing at birth right through to the Feedlotting phase. Live animal phenotypes utilised in the analysis include:
Live animal Weight records (including birth weight, 200 day, 400 day, 600 day and Mature Cow Weight).
Live animal ultrasound traits including eye muscle area, rib fat and rump fat.
Fertility traits including gestation length.
Maternal traits including Milk.
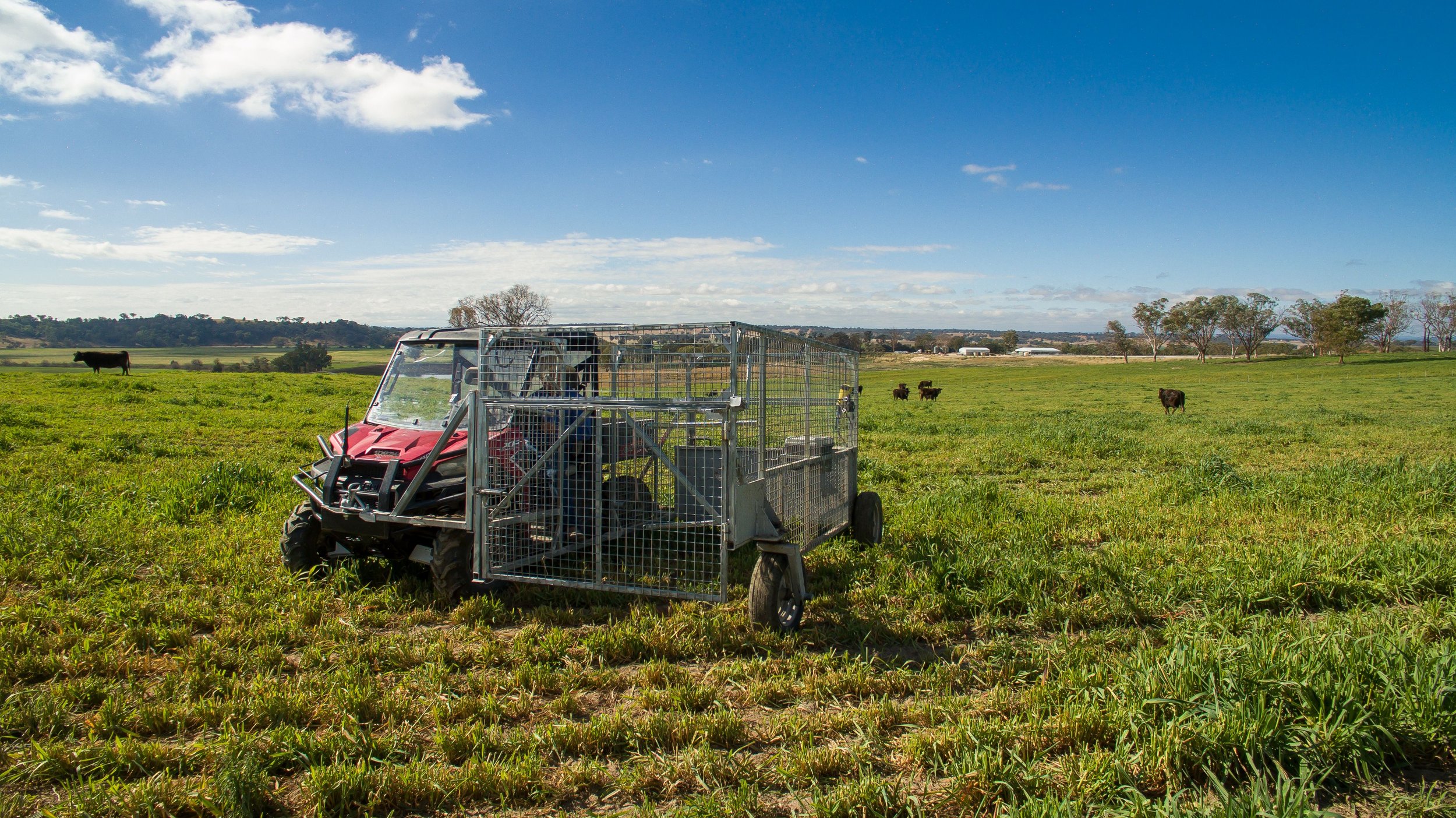
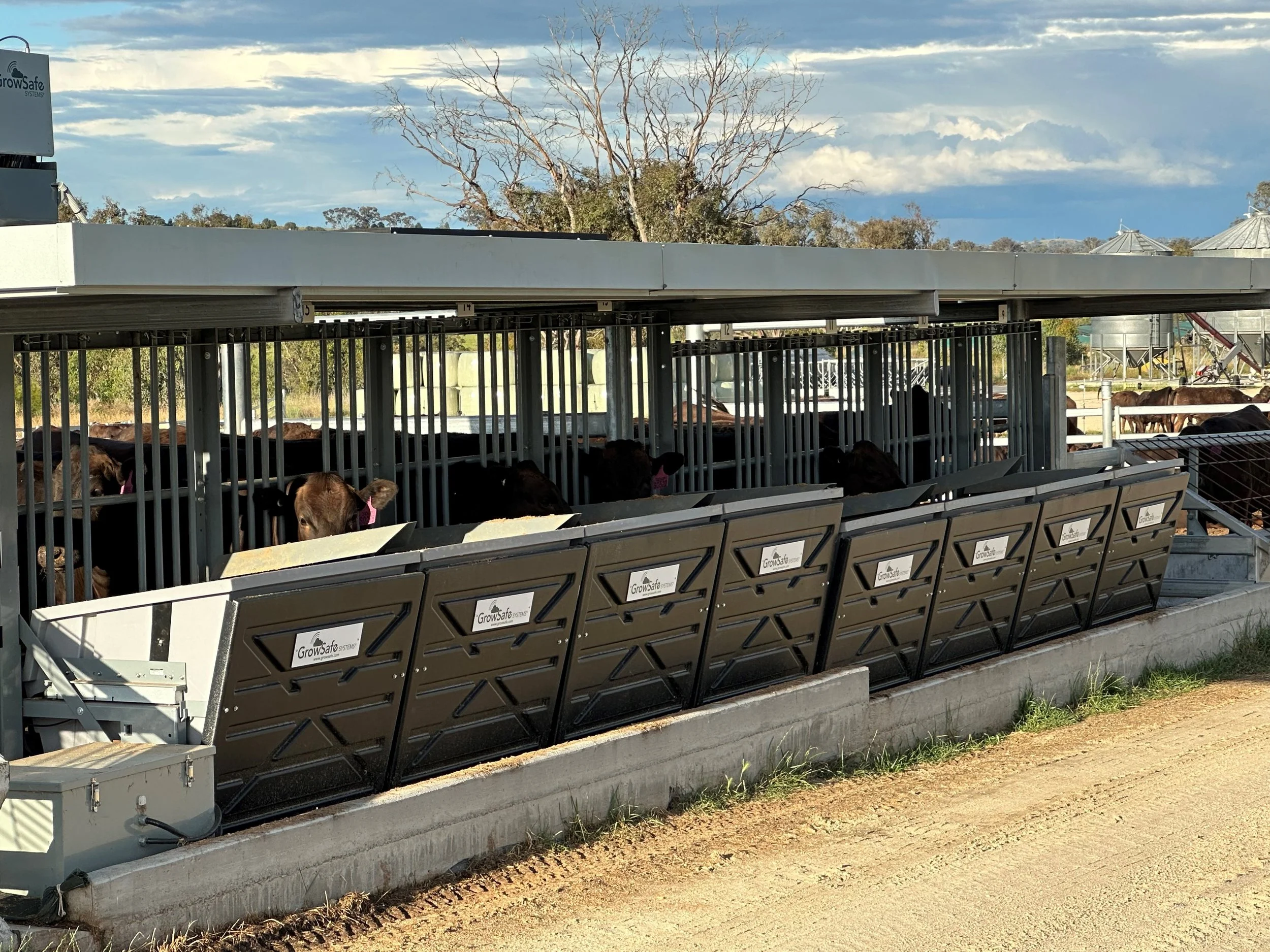
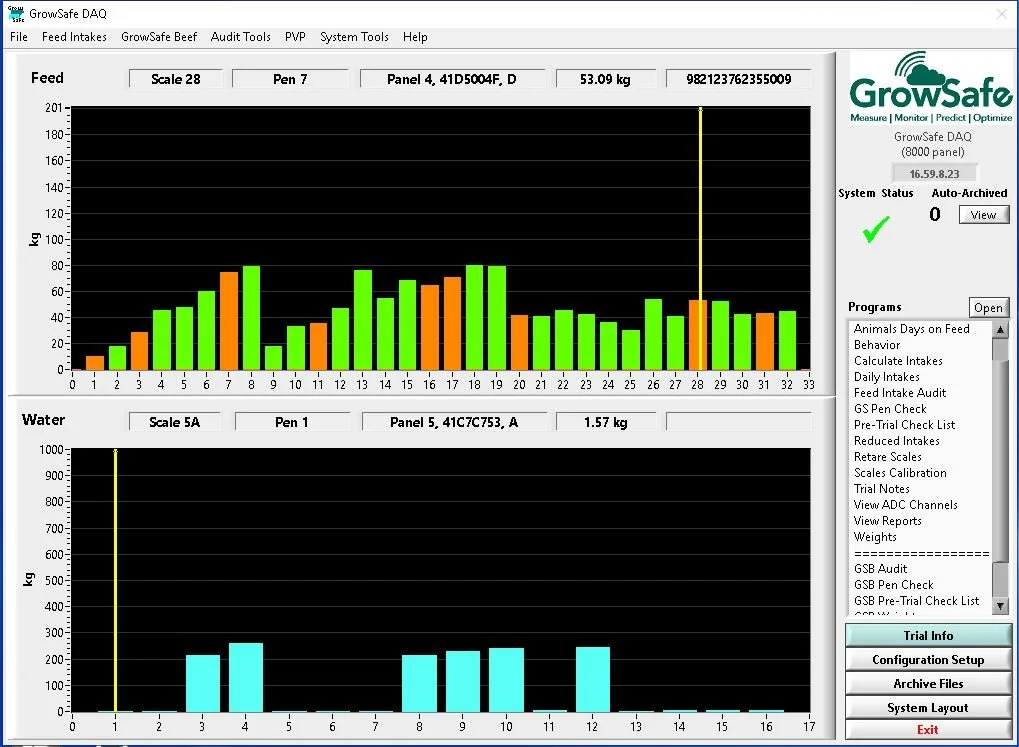
Feed intake traits – All progeny from the 3D Genetics Nucleus undertake a Feed Intake trial through the in-house Vytelle GrowSafe facility on farm at “Pukawidgi”.
The 3D Genetics program has collected more feed intake phenotypes than any other breeding program in Australia.
“The 3D Genetics program has collected more feed intake phenotypes than any other breeding program in Australia”
On the day of birth all calves are caught, weighed , tagged (ID and NLIS) and have an ear notch sample taken for Pesti-Virus PI testing.
Above is a screenshot of live data from the 3D Genetics’ Growsafe system during a feed efficiency trial in 2022.
Heifer Feed efficiency trial “Pukawidgi”.
Carcase phenotypes
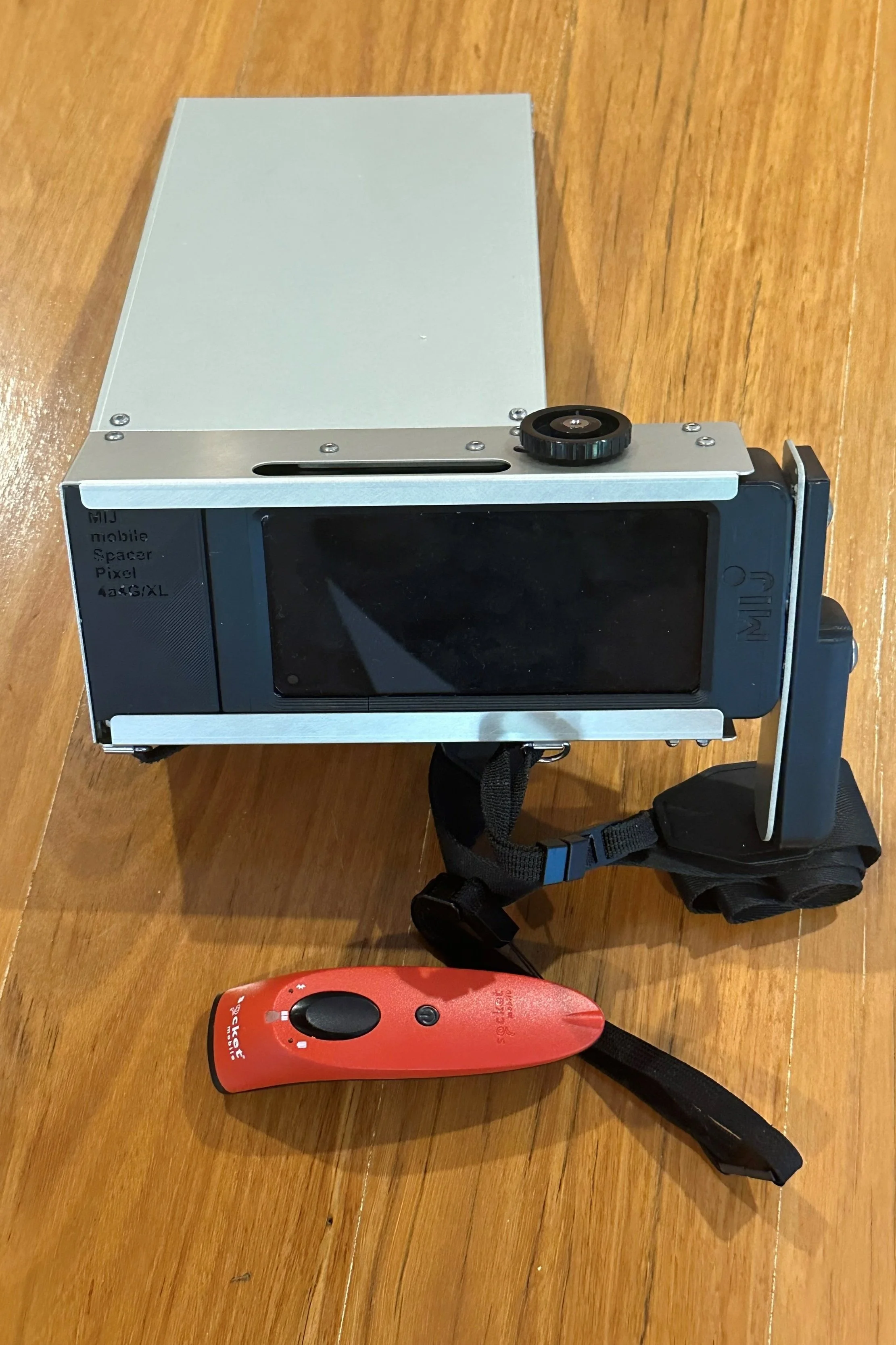
The 3D Genetics program follows progeny through the Abattoir system to ensure that grading results are obtained and recorded by the MIJ camera technology collating objective rather than subjective data for subsequent analysis. To date, the 3D Genetics’ program has collated and analysed over 30,000 carcase images. Utilising this approach, the economically important traits of commercial wagyu production of marbling, fineness of marbling and rib eye area are collected by the MIJ hardware in an objective manner. In addition, the AUSMEAT traits of Hot Standard Carcase Weight, rib fat and rump fat are utilised in the analysis.
MIJ Camera.
MIJ Beef analysis software displaying (left) coarseness and (right) fineness of marbling.
2. Genetic Analysis
Professor Wayne Pitchford, Joe Grose
3D Genetics has worked in collaboration with the University of Adelaide to undertake an innovative and Industry leading genetic analysis since 2015 known as ‘GRIP’ (Genomic Reporting Information Platform). 3D Genetics owns and has exclusive rights for use of the GRIP software platform in Wagyu cattle and programs involving Wagyu cross breeding. GRIP utilises the live animal and carcase phenotypes and the DNA genotypes as inputs for an advanced modern genetic evaluation system, based on Best Linear Unbiased Prediction (BLUP) statistical analysis to produce outputs such as:
Genomically enhanced Estimated Breeding Values (GEBVs) for a range of production traits
Parentage assignment
Genotypes of Interest including assignment of recessive diseases
Principle Component Analysis (PCA) utilised in multi breed analysis
Selection Index Calculation
DNA Helix
Heritability is a measure used in genetic analysis that estimates the degree of variation in a phenotypic trait within a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. The results from the 3D Genetics genetic analysis have revealed the important carcase MIJ camera trait of marbling has a heritability of 65%; this has allowed for rapid intergenerational genetic gain.
3. Mate Selection Software
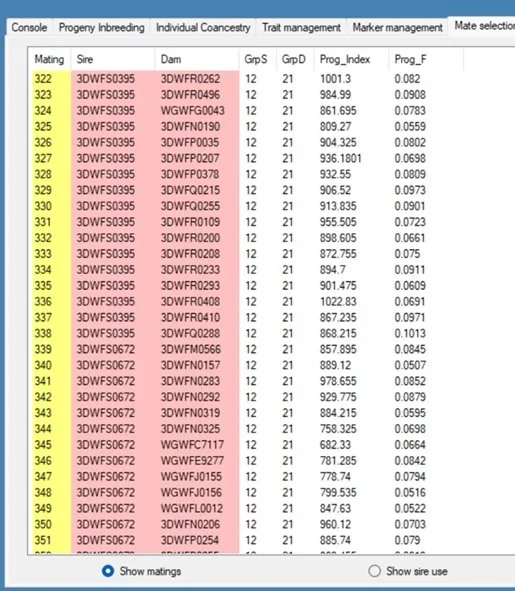
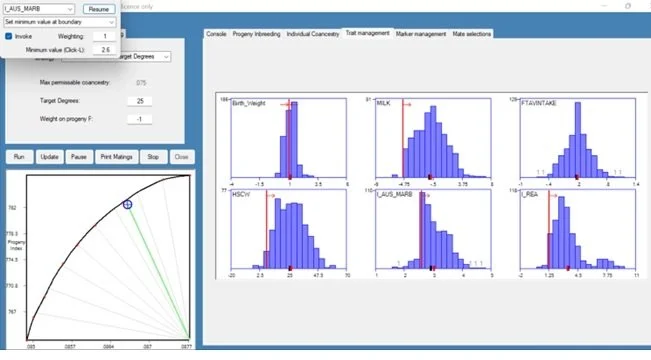
Breeding decisions are guided by Optimal contributions selection theory (OCS) which provides the 3D Genetics program with a framework for maximising genetic gain for a predefined rate of coancestry. Breeding for low coancestry in any one generation has a lasting impact over generations to increase genetic diversity and decrease the population mean inbreeding level. 3D Genetics utilises the MateSel software program to aid in the complex analysis of optimised mate selection decisions which has resulted in a herd with Industry leading performance whilst maintaining sustainable genetic diversity into the longer term.
MateSel - Joinings output file
Mate Selection software trait management